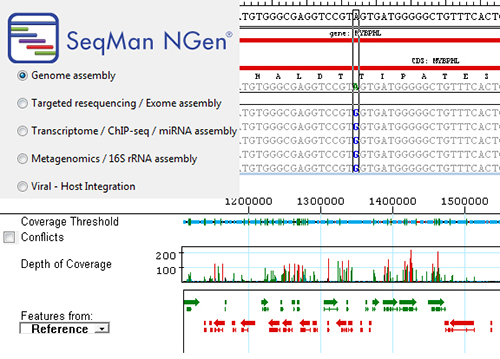
As next-generation sequencing (NGS) makes genetic testing for a wide range of human diseases increasingly commonplace, facile methods for validating the efficacy of those tests are essential. Federal regulatory standards embodied in the Clinical Laboratory Improvement Amendments (CLIA), for instance, are designed to ensure that these tests reliably achieve certain performance specifications in terms of accuracy, precision, and analytical sensitivity and specificity.
To facilitate the test validation process, the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST) through the Genome in a Bottle Consortium (GIAB) developed a highly curated set of genome-wide reference materials for the HapMap/1000 Genomes CEU female, NA12878. These materials include BED and VCF files of high confidence sequence regions and variant calls, respectively. NA12878 genomic DNA and a cell line are available (Coriell Institute) providing laboratories with an internal control for their processing and analysis pipeline.
Comparing testing results to the GIAB call sets allows establishment of both the analytical performance for regulatory certification as well as the appropriate assembly thresholds to apply when considering potential variants in clinical samples.
For the rest of the story, click here.